Physics Molecules and Matter Practice Exam Questions
Molecules and Matter Practice Exam Questions
Molecules are tiny particles that make up all matter around us, like water, air, and even ourselves. They're made of atoms bonded together, and how they're arranged determines the properties of different materials, like their shape, size, and behaviour.
Download and print our practice exam questions on the physics topic of molecules and matter.
Learn more

Visit our Energy page for revision notes and videos to help you study.
Molecules and Matter Practice Exam Worksheet
Practice exam style questions on energy.
Scroll down to reveal answers below.
Click to reveal answers
| Question | Answer | Extra information |
| 1 | Student A's measurements had a higher resolution [1 mark] Student B was more likely to misread the temperature [1 mark] |
|
| 2 | a random error [1 mark] | |
| 3 | 8.4°C [1 mark] | |
| 4 | 740 (seconds) [1 mark] | allow answers in the range 730 - 780 |
| 5 | 0.40 x 199 000 [1 mark]
79 600 (J) [1 mark] |
accept 79 600 (J) with no working shown for 2 marks |
| 6 | stearic acid has a higher temperature than the surroundings [1 mark]
temperature will decrease until stearic acid is the same as the room temperature / surroundings [1 mark] |
accept stearic acid is hotter than the surroundings |
| 7 | range of speeds [1 mark]
moving in different directions [1 mark] |
accept random motion |
| 8 | internal energy [1 mark] | |
| 9 | density = mass / volume [1 mark] | |
| 10 | 0.00254 / 0.0141 [1 mark] 0.18 [1 mark]kg/m³ [1 mark] |
accept 0.18 with no working shown for the calculation [2 marks] |
| 11 | Level 2: The method would lead to the production of a valid outcome. Key steps are identified and logically sequenced [3-4 marks]
Level 1: The method would not necessarily lead to a valid outcome. Some relevant steps are identified, but links are not made clear [1-2 marks] No relevant content [0 marks] Content can include:
|
|
| 12 | density = 2.70 (g/cm³) [1 mark] |
an answer of 2.70 (g/cm³) scores 2 marks |
| 13 | limestone [1 mark] | |
| 14 | eye position when using measuring cylinder or water level in can (at start) not at level of spout or not all water displaced by stone is collected in container [1 mark] |
|
| 15 | volume would be lower / higher [1 mark] | |
| 16 | Level 3: Clear and coherent description of both methods including equation needed to calculate density. Steps are logically ordered and could be followed by someone else to obtain valid results. [5-6 marks]
Level 2: Clear description of one method to measure density or partical description of both methods. Steps may not be logically ordered. [3-4 marks] Level 1: Basic description of measurements needed with no indication of how to use them. [1-2 marks] No relevant content [0 marks] Content can include for both:
Metal cube:
Small statue:
|
allow P = W/ T |
| 17 | any two from:
[2 marks] |
reduces human error is insufficient
allow to assess the repeatability of the data
|
| 18 | random error [1 mark]
(because) eye position would not be the same each time (relative to the liquid) [1 mark] |
allow a parallax error human error is insufficient
allow systematic error only if it is clear that the student always viewed liquid level from above meniscus (or below) |
| 19 | (a temperature increase would) increase the pressure in the tube (even if the volume was constant) [1 mark]
(because a highter temperature would mean) higher (average) kinetic energy of molecules / particles [1 mark] |
allow higher (average) speed for higher (average) kinetic energy |
| 20 | 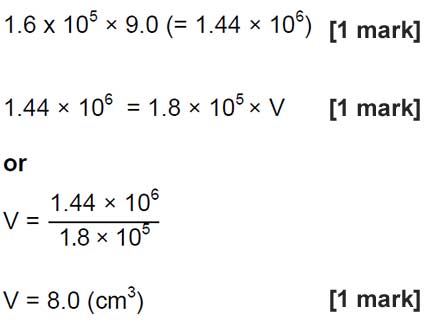 |
an answer of 8.0 (cm³) scores 3 marks
allow for 2 marks |
| 21 | work is done on the air (in the tyre) [1 mark] so the temperature (of the air) increases [1 mark] |
allow the (average) kinetic energy of the particles increases |