
Force and Motion
Newton's laws are the foundational principles for our understanding of the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. They are the rules of a game that all objects play by. The laws are used to understand, predict and solve problems related to motion.
Equations on this page:
Resultant Force and Momentum.
Practicals on this page:
Investigating force & acceleration
Newton's First Law
Newton's First Law is:
If the resultant force on a stationary object is zero, the object will remain stationary.
If the resultant force on a moving object is zero, it'll just carry on moving at the same velocity.
This law is about how things like to keep doing what they're already doing. If you're sitting still, you'll stay still unless someone pushes you. If you're moving, you'll keep moving in the same way unless something stops you or changes your direction.
Newton's Second Law
Newton's Second Law is:
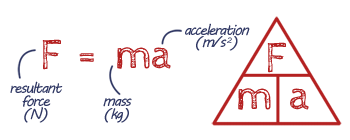
Newton's Second Law tells us how much oomph (force) you need to make something move or change the way it's moving. It's like saying, if you want to make a heavy ball move fast, you need to give it a big push. If it's light, you don't need as much force.
Newton's Third Law and Inertia
Newton's Third Law is:
When two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite.
Newton's Third Law means that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal force in the opposite direction back on the first object.
Imagine you're sitting in a chair. When you push down on the chair, the chair pushes back up on you with an equal force. This is why you don't fall through the chair. Similarly, when you walk, your foot pushes backward against the ground, and the ground pushes forward on your foot, propelling you forward.
So, Newton's third law tells us that forces always come in pairs. If you push on something, it pushes back on you with the same force but in the opposite direction.
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. Objects with more mass have more inertia, meaning they are harder to accelerate or decelerate.
Imagine you're in a car that suddenly stops. If you're not wearing a seatbelt, you'll feel like you're being pushed forward. This is because your body wants to keep moving at the same speed and in the same direction as the car was going. This resistance to change in motion is inertia.
Similarly, if you try to push a heavy box, it's harder to get it moving than a lighter box because the heavy box has more inertia.
Key Words
Resultant Force - the overall force on a point or object.
Mass - the amount of 'stuff' in a object.
Weight - the force acting on an object due to gravity.
Gravitational Force - the force of attaction between masses.
Equilibrium - when the forces on an object are balanced.
Friction - the force resisting  movement between objects.
Reaction time - the time it takes for a person think see something then do something.
Momentum - how much 'oomph' an object has.
EQUATION Resultant Force (Newton's Second Law of Motion)
Newton's Second Law of Motion tells us how much oomph (force) you need to make something move or change the way it's moving. It's like saying, if you want to make a heavy ball move fast, you need to give it a big push. If it's light, you don't need as much force.
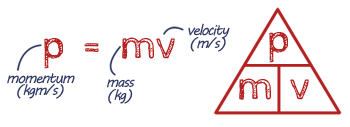
EQUATION Momentum
Momentum is a way of measuring how much motion an object has. It depends on two things: how heavy the object is and how fast it's moving. This means a bigger or faster object has more momentum, and it's harder to stop. Momentum is always conserved in collisions, which means the total momentum before and after stays the same (as long as no external forces act).
PRACTICAL Investigating force & acceleration
Watch the video and have a go at writing out the steps of the practical.



