Motion
Motion in physics is just how things move. It could be moving in a straight line, spinning around, or even going back and forth. So, if something changes its position over time, we say it's in motion.
Equations on this page:
Distance using speed & time and Acceleration.
What is distance and displacement?
Distance is the total length of the path travelled by an object. It's a scalar quantity. It doesn't consider direction, only how much ground is covered. For example, if you walk from your house to the park and then back home, the total distance you covered is the sum of the distance from your house to the park and from the park back to your house.
Displacement is a measure of how far an object is from its starting point in a straight line. It's a vector quantity. It considers both the distance and the direction from the starting point to the ending point. So, if you walk from your house to the park and then back home, your displacement is zero because you've ended up where you started. But if you walk from your house to the park and then to your friend's house, your displacement is the straight-line distance from your house to your friend's house, regardless of the path you took.
What is speed and velocity?
Speed is how fast an object is moving, regardless of direction. It's calculated by dividing the distance travelled by the time taken. For example, if you drive 100 km in 1 hour, your speed is 100 km/h (kilometres per hour).
Velocity is similar to speed but includes direction. It's the rate of change of displacement. So, it's calculated by dividing the displacement by the time taken. For example, if you walk 4m east in 2 seconds, your velocity is 2m/s (meters per second) east. If you walk 4m west in 2 seconds, your velocity is 2m/s west.
Typical speeds
Walking - 1.5m/s
Running - 3m/s
Cycling - 6m/s
Car - 25m/s
Train - 55m/s
Plane - 250m/s
Key Words
Acceleration - how quickly you're speeding up.
Uniform Acceleration - constant acceleration.
Distance-Time Graph - if an object moves in a straight line, its distance travelled can be plotted on a distance-time graph.
Velocity-Time Graph - when a object's velocity changes it can be plotted in on a velocity-time graph.
Friction - slow things down. It always acts in the opposite direction to the movement.
Drag - Increases as speed increases.
Terminal Velocity - Maximum speed an object will fall at. Maximum speed depends on the shape and area of an object.
Also see Forces, Force & Motion
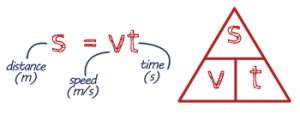
EQUATION Distance using speed & time
Distance tells us how far something has travelled. It depends on how fast it was going and for how long. This is shown in the equation: Distance = Speed × Time. So, if you travel faster or for a longer time, the distance you cover will be greater.
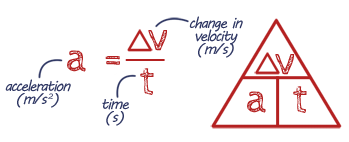
EQUATION Acceleration
Acceleration is how quickly something speeds up or slows down. It’s calculated using the change in speed over time, with the equation: Acceleration = (Final Speed – Initial Speed) ÷ Time. This shows how much the speed changes each second – the bigger the acceleration, the faster the speed increases (or decreases if it’s slowing down).