
Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of all living organisms on Earth – from plants and animals to microorganisms. Explore why biodiversity is important for stable ecosystems, how human activities can threaten it, and what we can do to protect it. This topic helps you understand the balance of life and the need for conservation.
What Is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the variety of all different species of organisms on Earth, or within a specific habitat. High biodiversity helps keep ecosystems stable by ensuring that organisms depend on each other in balanced food chains and webs.
Threats to Biodiversity
Human activities have caused a significant decline in global biodiversity. These include:
1. Waste Management
As the population grows, more household waste, sewage, and chemical pollution are produced. This pollutes land, air, and water, reducing biodiversity and damaging habitats.
2. Deforestation
Large areas of forests are cleared for agriculture, timber, and space. This destroys habitats and contributes to increased carbon dioxide levels.
3. Peat Bogs
Peat bogs store carbon and are home to many species. Draining them for compost or farming leads to a loss of biodiversity and releases stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Global Warming and Climate Change
 Increased levels of greenhouse gases (like carbon dioxide and methane) trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, causing global warming.
Increased levels of greenhouse gases (like carbon dioxide and methane) trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, causing global warming.
Consequences of Global Warming:
- Melting ice caps and rising sea levels
- Changes in species distribution and migration
- Loss of habitats
- More extreme weather events
All of these affect biodiversity and food chains around the globe.
Revision Notes

The Cornell method is like a supercharged note-taking system that helps you ace your revision!
Print out our blank revision notes pages to help you revise.
How to make effective revision notes with the Cornell method.
Exam Questions & Answers

Download and print off practice our FREE worksheet with exam style questions on Cell Biology.
Maintaining Ecosystems & Protecting Biodiversity
We can help reduce biodiversity loss by:
- Breeding programmes for endangered species
- Protecting habitats (e.g. nature reserves)
- Reforestation
- Reducing waste and pollution
- Encouraging sustainable farming and fishing
Trophic Levels and Biomass
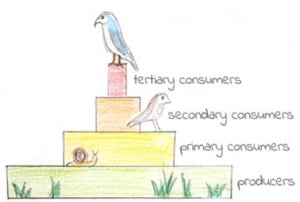 In a food chain, trophic levels describe an organism's position:
In a food chain, trophic levels describe an organism's position:
- Level 1 – Producers (e.g. plants)
- Level 2 – Primary consumers
- Level 3 – Secondary consumers
- Level 4 – Tertiary consumers
As you move up, energy and biomass decrease. Only about 10% of biomass is transferred at each level — the rest is lost through respiration, movement, waste, or as heat.
Pyramids of Biomass
These show the total biomass at each trophic level in a food chain. They are always pyramid-shaped because energy is lost at each stage.
Food Security & Food Production
Food security means having reliable access to enough safe and nutritious food. It's affected by:
- A growing population
- Changing diets (e.g. more meat consumption)
- Climate change
- Farming practices
- Pests and diseases
- Overfishing
Overfishing
Catching too many fish reduces fish stocks. This can lead to species becoming endangered and disrupts marine food chains.
Farming and Biotechnology
To improve food security and reduce environmental damage, modern farming uses:
- Fertilisers and pesticides (though these can cause pollution)
- Selective breeding for crops and livestock
- Biotechnology, including:
- Genetically modified (GM) crops – e.g. rice with added vitamins or drought resistance
- Mycoprotein – a high-protein food made using fungi, often used as a meat substitute
Biotechnology helps increase food yield and efficiency while using fewer natural resources.
Revision Notes

The Cornell method is like a supercharged note-taking system that helps you ace your revision!
Print out our blank revision notes pages to help you revise.
How to make effective revision notes with the Cornell method.


